Up to Standards
- Subject: Identification of Aisin manual transmissions and transfer cases
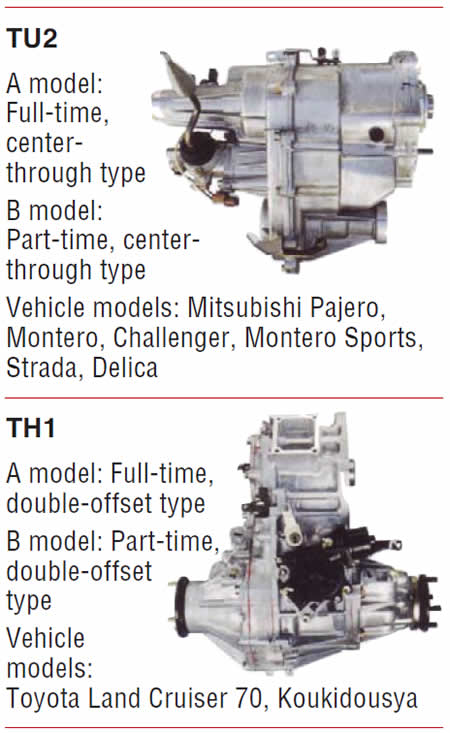
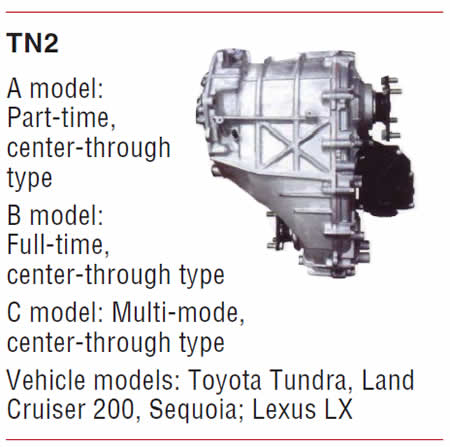
- Units: AZ6, AG5, AW5, AR5, AY6, AM5, AM15, AH16, AH15, AH5, SP6, BC25, BC5, BC16, BJ6, BE35, BH6, BG6, MC5, MC25, TJ1, TJ2, TB1, TU2, TH1, TN2
- Vehicle Applications: BMC, Chevrolet, Chrysler, Citroen, Daihatsu, Dodge, GMC, Hino, Holden, Hummer H3, Jeep, Lexus, Lotus, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Opel, Peugeot, Pontiac, Porsche, Saturn, Suzuki, Toyota
- Essential Reading: Shop Owner, Center Manager, Rebuilder, Diagnostician, R&R
- Author: Mike Weinberg, Rockland Standard Gear, Contributing Editor
The manufacture of cars and trucks has become a truly worldwide venture. There are suppliers all over the globe providing parts and components for vehicles that are produced and sold around the globe. Some names are quite familiar to us, such as BorgWarner, ZF, Tremec, New Process Gear and New Venture Gear, because of their large presence here in the U.S.
Other suppliers of transmissions and transfer cases have a significant presence in the market but are not as well known, such as Aisin Seiki Corp. Aisin Seiki is a publicly traded company, with 76% of the shares held by the public and 24% held by Toyota Motor Co. Aisin Seiki has several divisions: AW (Aisin Warner), which manufactures automatic transmissions for the world’s automakers; Aisin AI, which manufactures the manual transmissions and transfer cases for those same automakers; and AWA, which is the Aisin world entity for sales of aftermarket parts to the Americas. The various divisions operate in numerous countries around the globe.
One of the major problems associated with buying and selling units and parts in our industry is the need to properly identify the unit you are working on. This article is devoted to identifying current-production models of manual transmissions and transfer cases produced by Aisin AI, with the hope of making it easier for you to obtain parts in the aftermarket. Past production is not listed but includes the familiar AX5, AX15 and R151 Toyota transmissions.
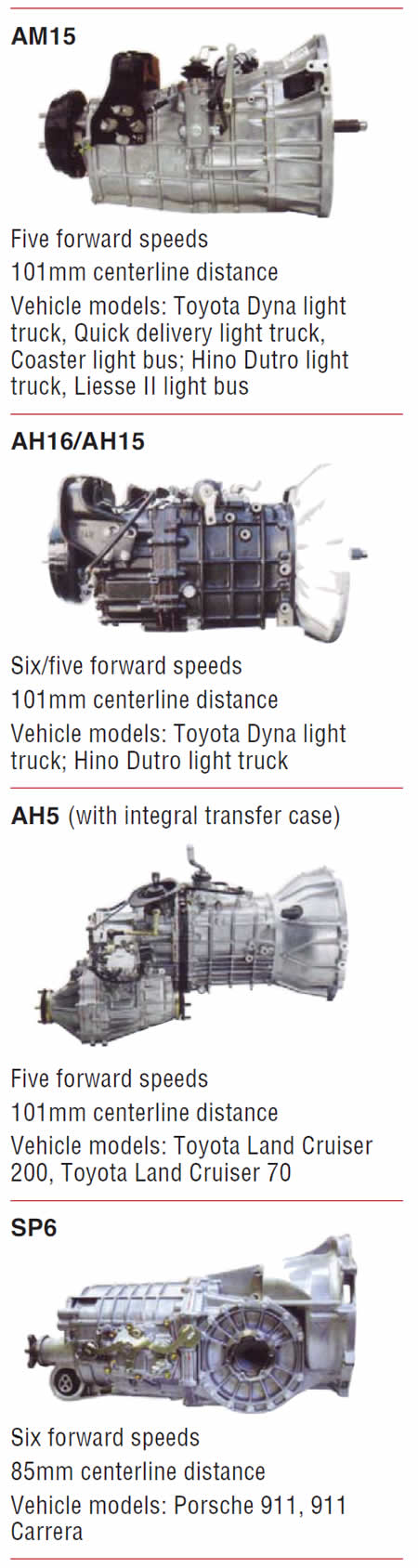
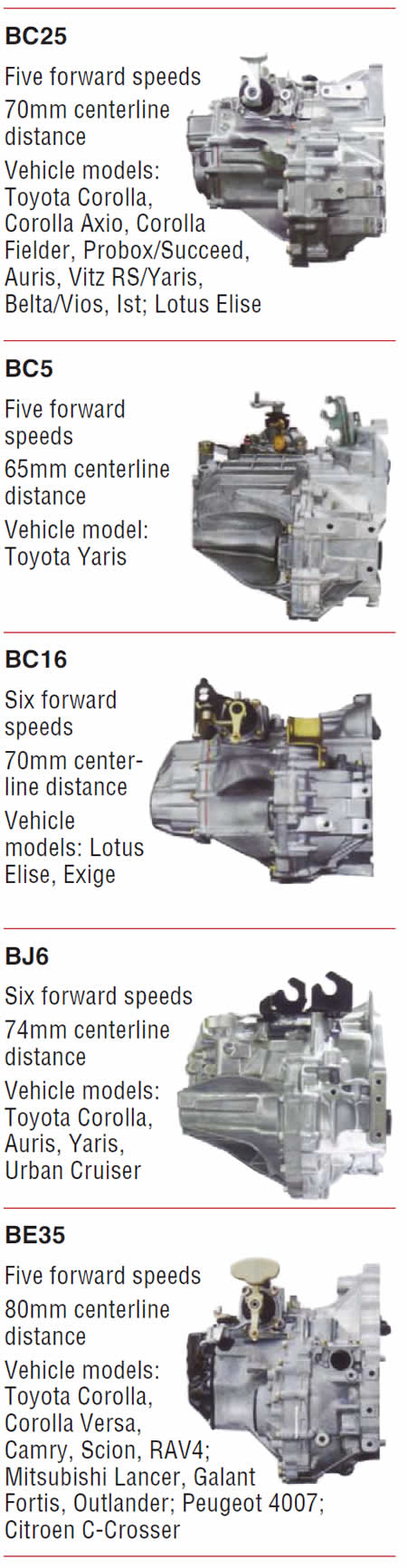
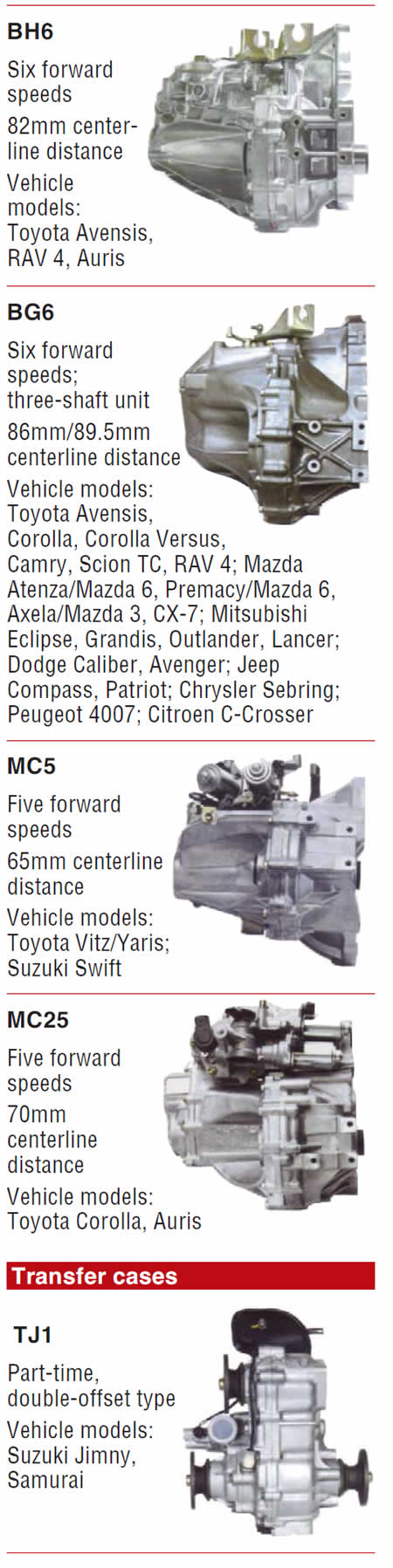
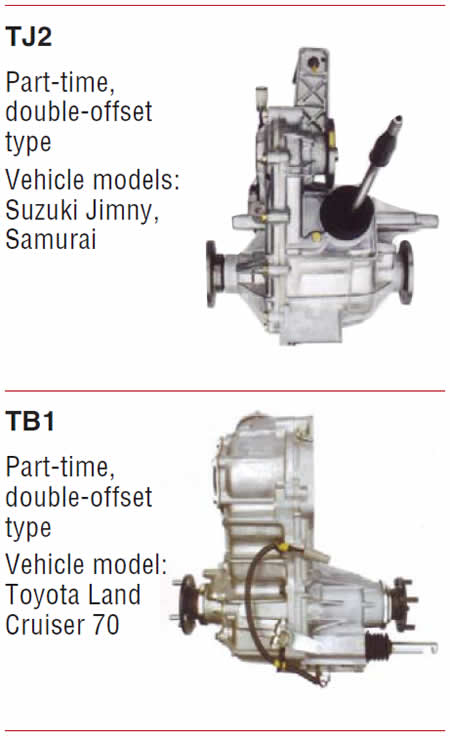
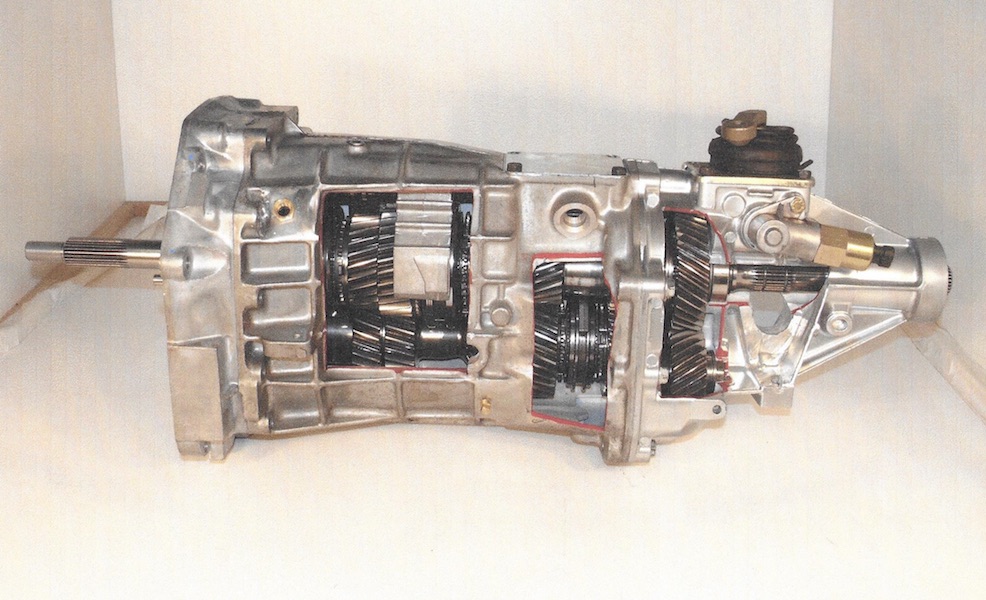
Note: The units are displayed with centerline distances listed. The centerline distance is the measurement from the center of the input shaft to the center of the countershaft. The greater the distance, the greater the torque capacity of the transmission, as the centerline determines the width (diameter) of the internal gears.