R&R Tech
- Subject: Harsh engagement and shifts
- Unit: 4R100
- Vehicle Application: 1998 Ford E-350 van
- Essential Reading: Diagnostician, R & R
- Author: David Finley
Those of us in the business have seen all different kinds of oddball installations and strange diagnoses that make absolutely no sense. There are so many variables that can contribute to a problem, and finding the root cause is an ongoing challenge for all of us. To complicate things even further, if you don’t have the background story on the vehicle you’re trying to fix, you’re working with assumptions that can easily get you into trouble. This story is an example of one such repair challenge.
Our shop sees a lot of vehicles that are older. Chances are high that they have experienced a major repair at some point. Sometimes they involve used-component transplants because the vehicle owner was trying to save money or a good-intentioned relative had something lying around that would “fit.” Whatever the case, those vehicles are a reality, and sometimes they find our way to us.
The owner of a 1998 Ford E-350 gave us a call, saying his van was shifting roughly, and asked whether we could take a look at it and diagnose the problem. We set an appointment for him, and when the van was dropped off the only information he gave was that the van had a rough shift – no more, no less. We gathered the usual information such as VIN, year, make, model and engine size. We wrote up the repair order and started the diagnostic routine.
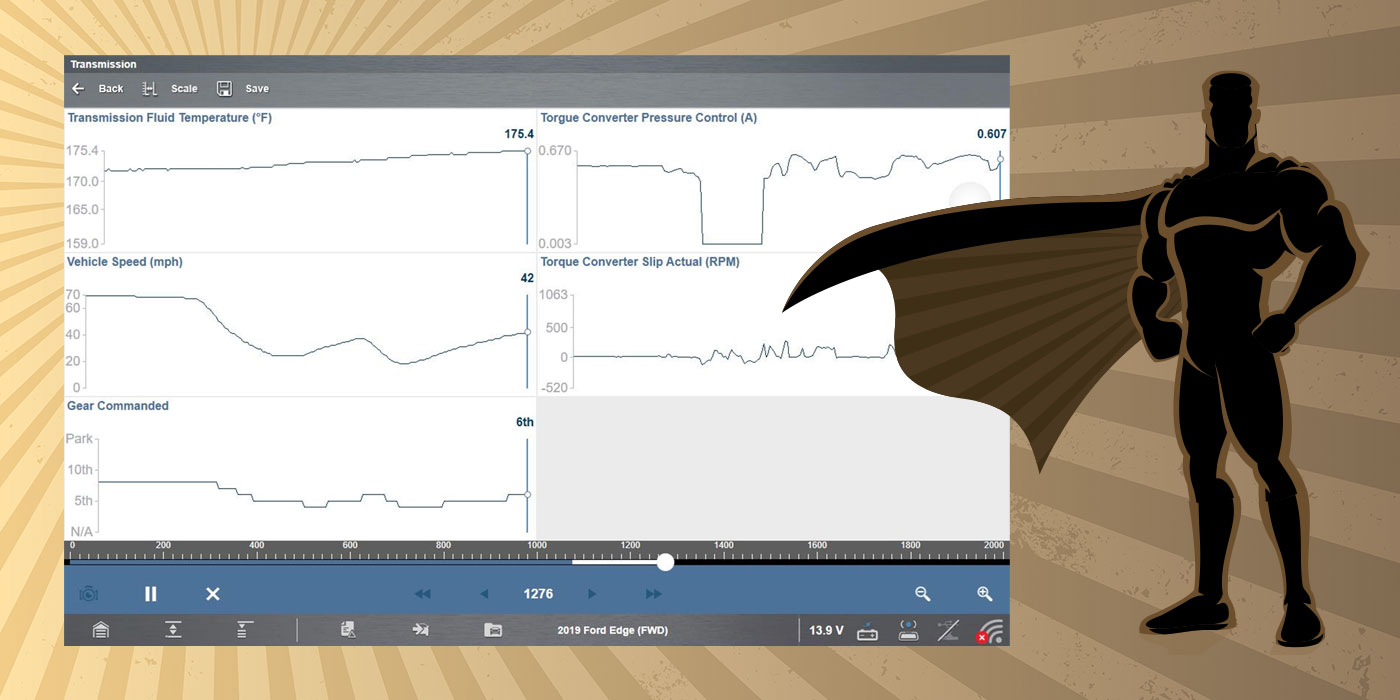
The first step in any repair process is to duplicate the concern, so I took off on a road test to see what I could find. I noticed a harsh engagement right away when I shifted the transmission into gear, and as the customer had said, the shifts were rough and harsh. The shift feel was similar to that of a Ford that had high line pressure due to a code being set, which also would explain the check engine light (CEL) being illuminated. I hoped that a quick scan would provide the information I needed.

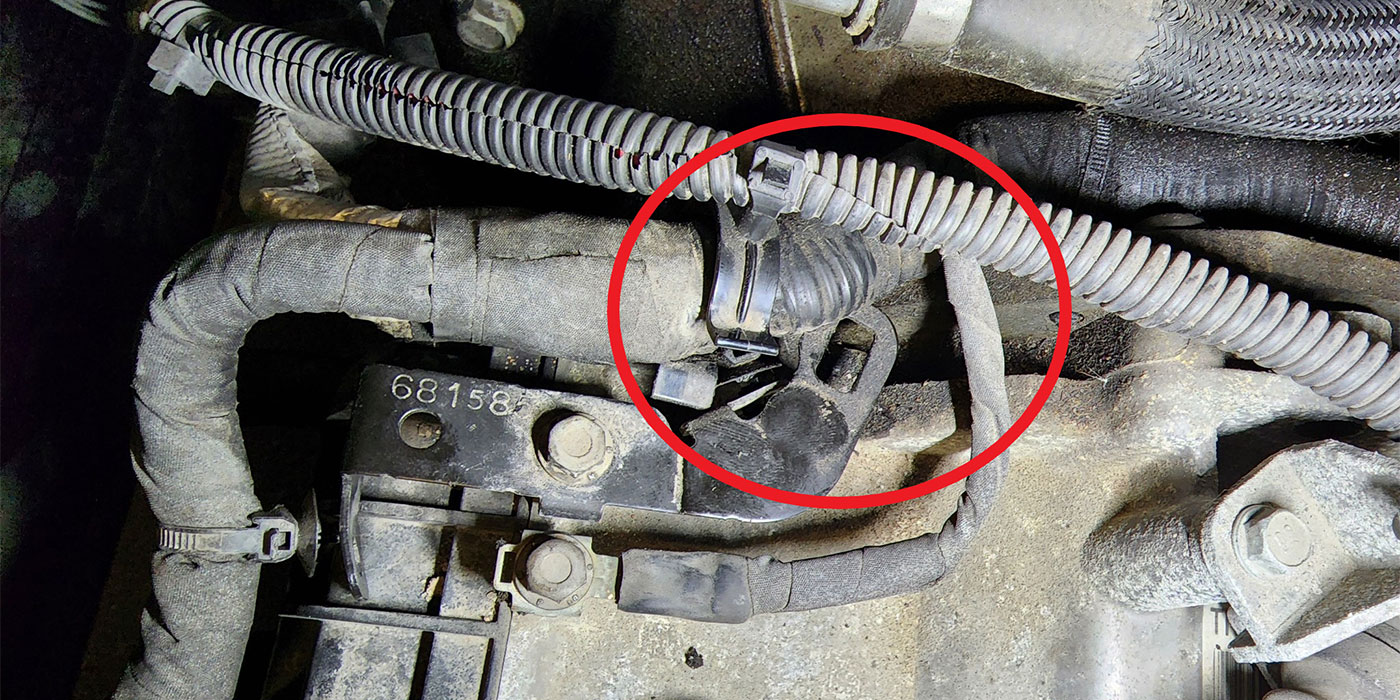
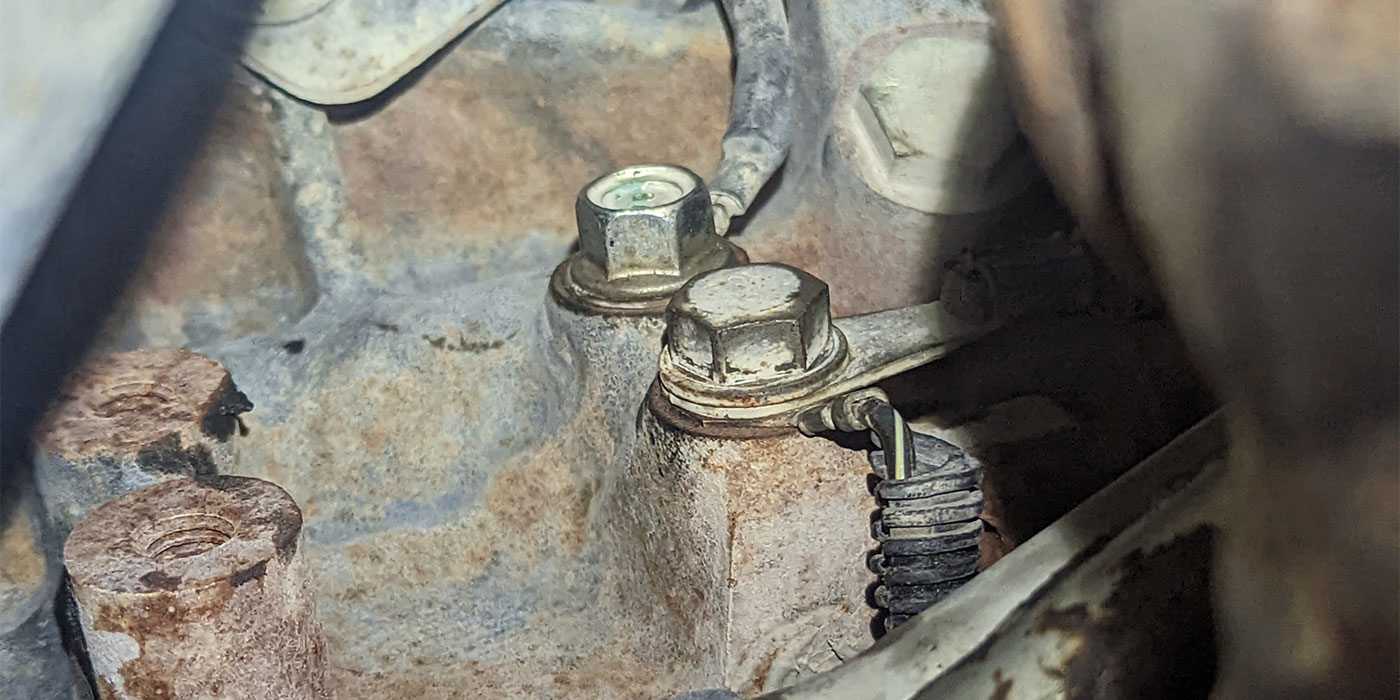
The only hard fault that existed in the system was for the output-speed sensor (OSS), code P0720, and the CEL was on. With the van on the rack, a quick visual inspection revealed nothing out of the ordinary beyond the fact that it appeared I was working with an E4OD that didn’t use an OSS. All the wiring appeared to be intact and in place, nothing unplugged or loose. Something was fishy here, and I was beginning to wonder whether something had been changed or modified on this rig.
Our company uses a proprietary ID system called “SMTC” to create our own parts-numbering system for the units we build, and also to identify which transmissions fit a given application. Our application system showed that this van could be equipped with either an E4OD or a 4R100, so at that point I looked to see whether the transmission ID tag was still in place. It was, and it crossed over to a 4R100. I thought I was close to solving the issue, because at the time I thought that all 4R100 units were equipped with input- and output-speed sensors. There just had to be an unplugged harness somewhere for those sensors.
I was wrong. Further research revealed that the 4R100 units in the 1998 and 1999 model years did not use those sensors. So how could I have a code for components that the vehicle wasn’t built with? It wasn’t making any sense, so I asked my store manager to contact the van owner to see whether we could get more information from him.
Sure enough, the truth came out. It turns out that the engine in this van was transplanted from a 2000-model-year school bus. The van’s transmission, however, was still original. I found out that model-year-2000 and newer 4R100 units did in fact use input- and output-speed sensors. Now some things were getting clearer, so I decided to take a look at the numbers on the PCM. And there was the answer.
The newer PCM from the donor vehicle had been installed in this van along with the newer engine. Since this PCM was looking for a signal from the OSS (from a 2000-model-year transmission) and there wasn’t any signal for it to receive, it was coding P0720, turning on the CEL and going into failsafe mode. We ordered and installed the correct PCM for the vehicle. There were no codes, the engine ran great and the transmission shifted perfectly. A PCM of the correct model year and calibration solved our problem, proving once more that there is no such thing as too much information.

David Finley is the head diagnostician at Certified Transmission’s location in Bellevue, Neb., and is also an experienced transmission builder. He has been with the company more than 20 years.